21 اکتبر 2025, مقالات ISI
Imeglimin as an Effective Therapeutic Approach in Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and Aim
Imeglimin, a novel oral antidiabetic belonging to the “glimin” class, has emerged as a promising therapeutic option for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). It exerts dual effects by improving insulin secretion and enhancing mitochondrial function. This umbrella review, systematic review, and meta-analysis aimed to comprehensively assess the efficacy and safety of imeglimin in the management of T2DM.
Methods
A systematic literature search was performed in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane Central up to June 2025. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with follow-up durations ≥12 weeks were included. Outcomes of glycemic control, insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, and lipid profiles were analyzed using random- or fixed-effects models depending on heterogeneity. Quality assessment was performed via the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2.0 tool, AMSTAR2, and evidence strength was rated using the GRADE framework.
Results
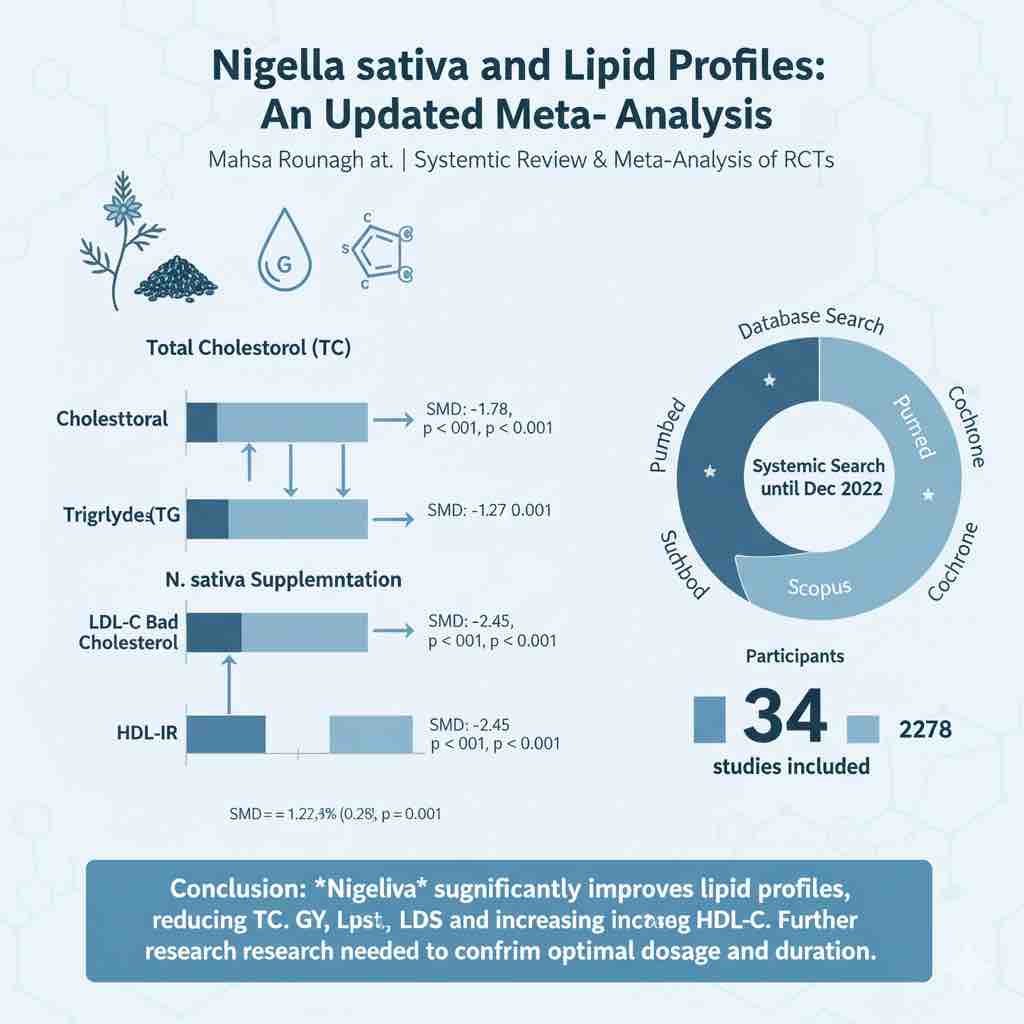
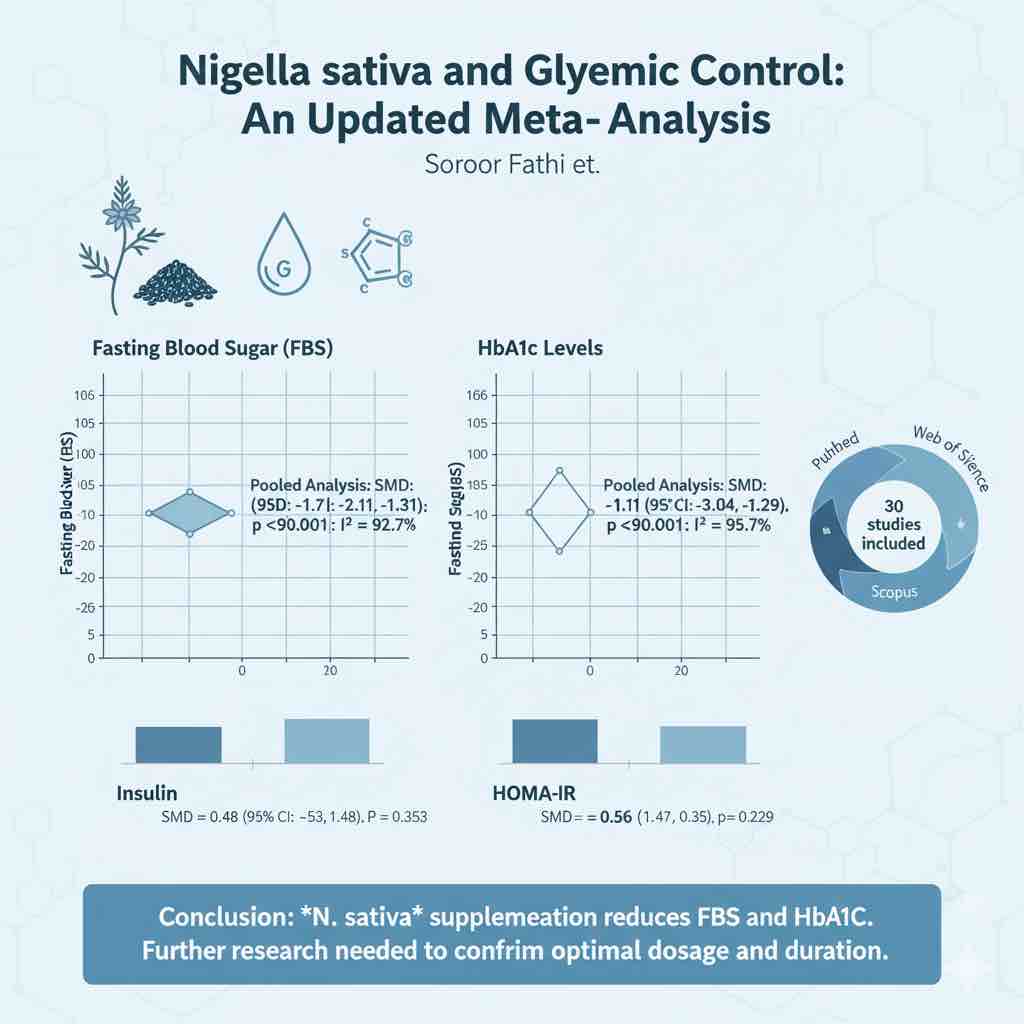
Twelve RCTs (n = 1,774 participants) were identified. Imeglimin significantly decreased fasting plasma glucose (FPG) (SMD: −0.51; 95% CI: −0.72, −0.29; p < 0.001) and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (SMD: −0.45; 95% CI: −0.86, −0.05; p = 0.031), and improved β-cell function (HOMA-β) (SMD: 0.59; 95% CI: 0.18, 1.01; p = 0.020). No significant changes were observed in insulin, HOMA-IR, or C-peptide levels (p > 0.05). LDL-cholesterol slightly increased (SMD: 0.32; 95% CI: 0.11, 0.53; p = 0.017), while HDL-C and triglycerides were unaffected. Safety analyses showed no significant differences in serious or non-serious adverse events between imeglimin and control groups.
Conclusion
Imeglimin demonstrates favorable efficacy for glycemic control and β-cell function, with an acceptable safety profile in adult T2DM patients. However, a mild LDL-C increase warrants further investigation. Large-scale, long-term clinical trials across diverse populations are required to confirm these outcomes.
Keywords
Imeglimin; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Glycemic control; β-cell function; Systematic review; Meta-analysis.