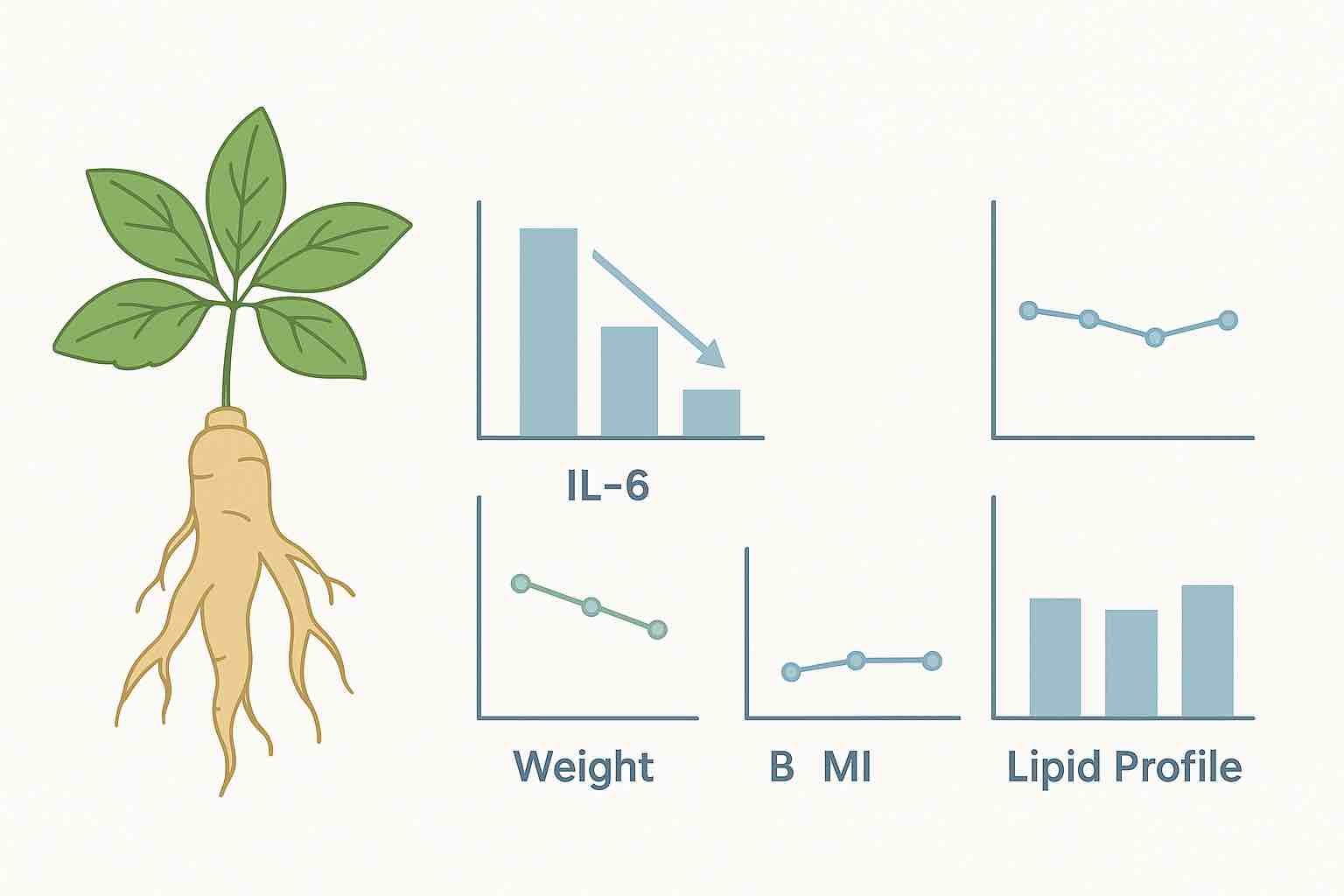
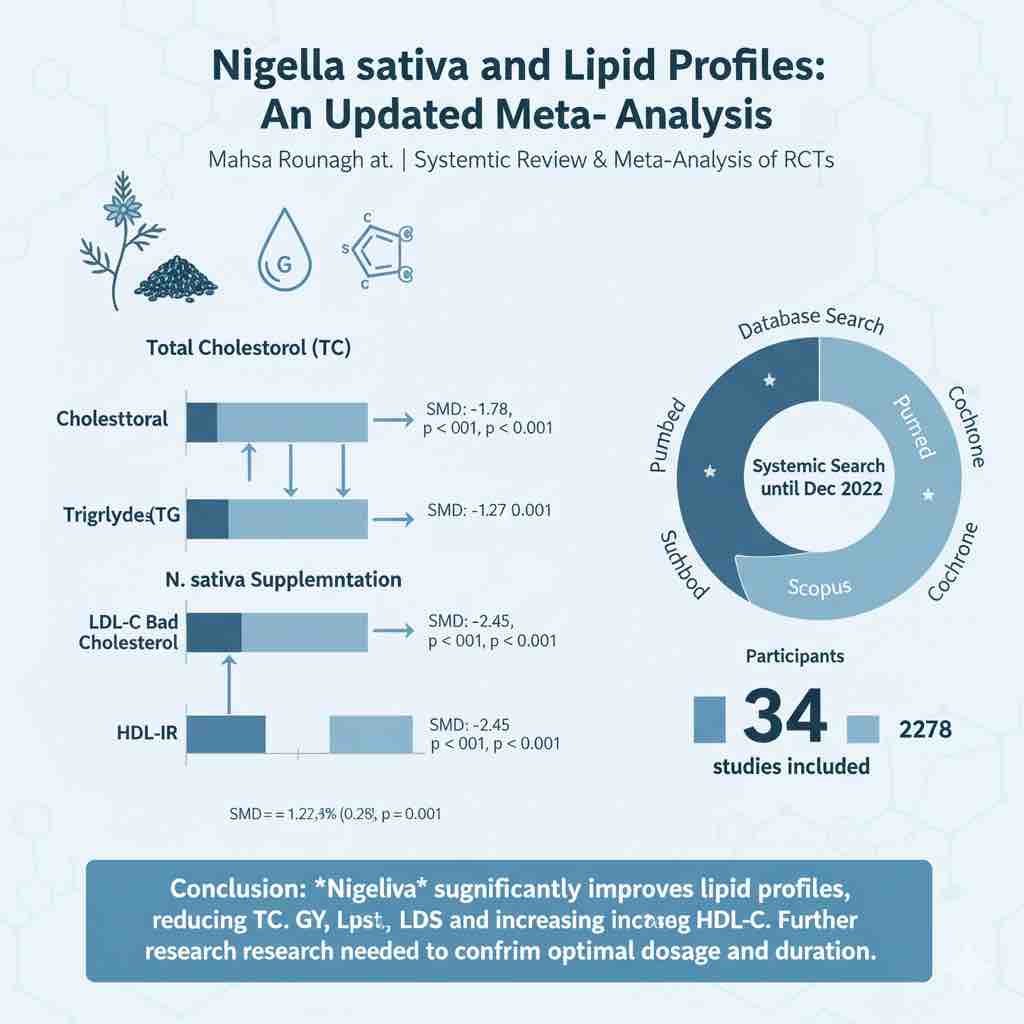
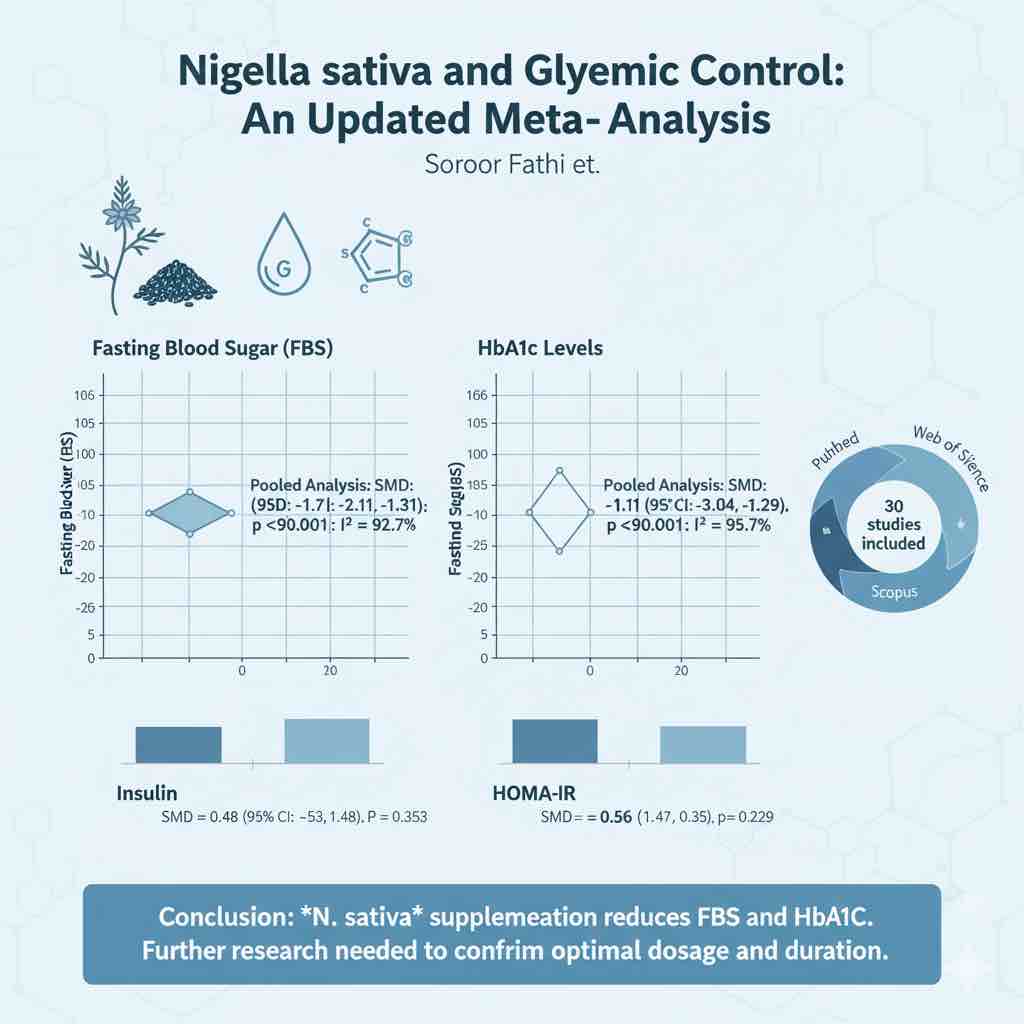
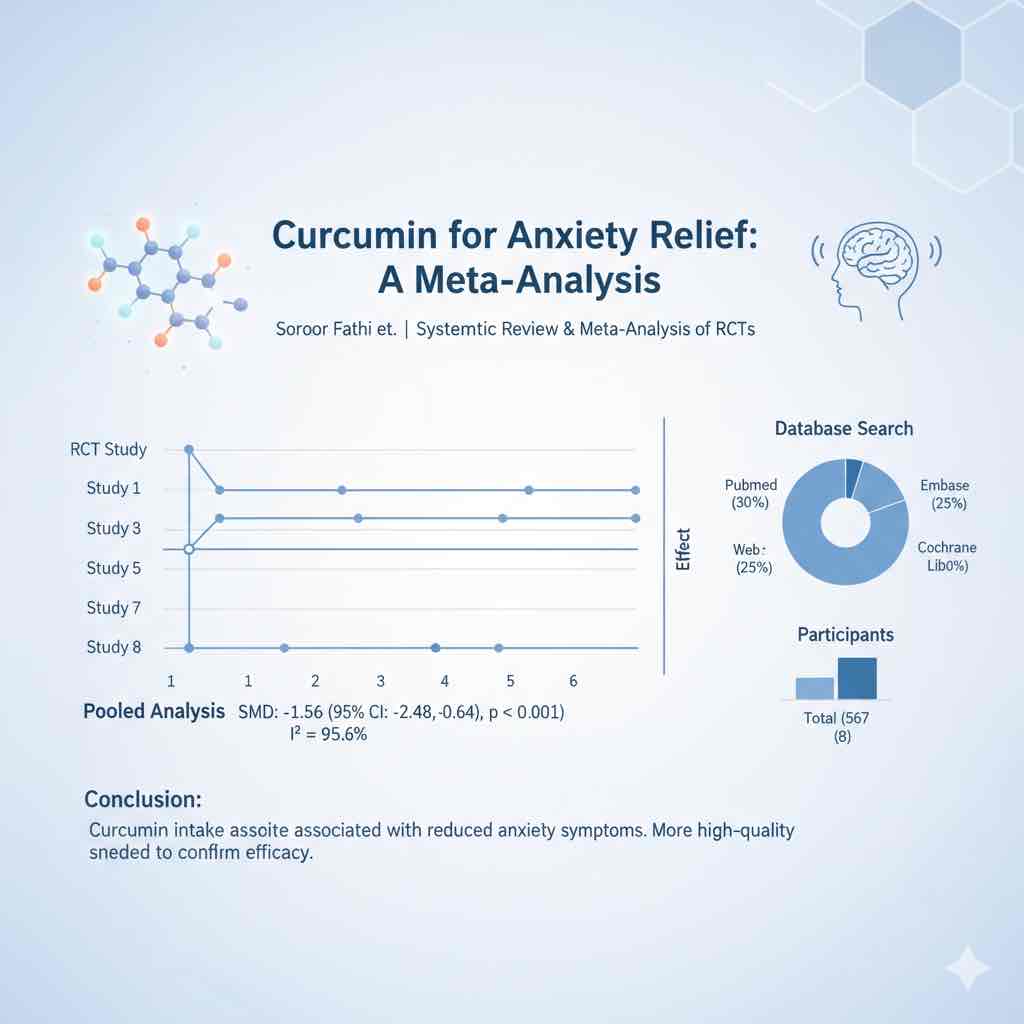
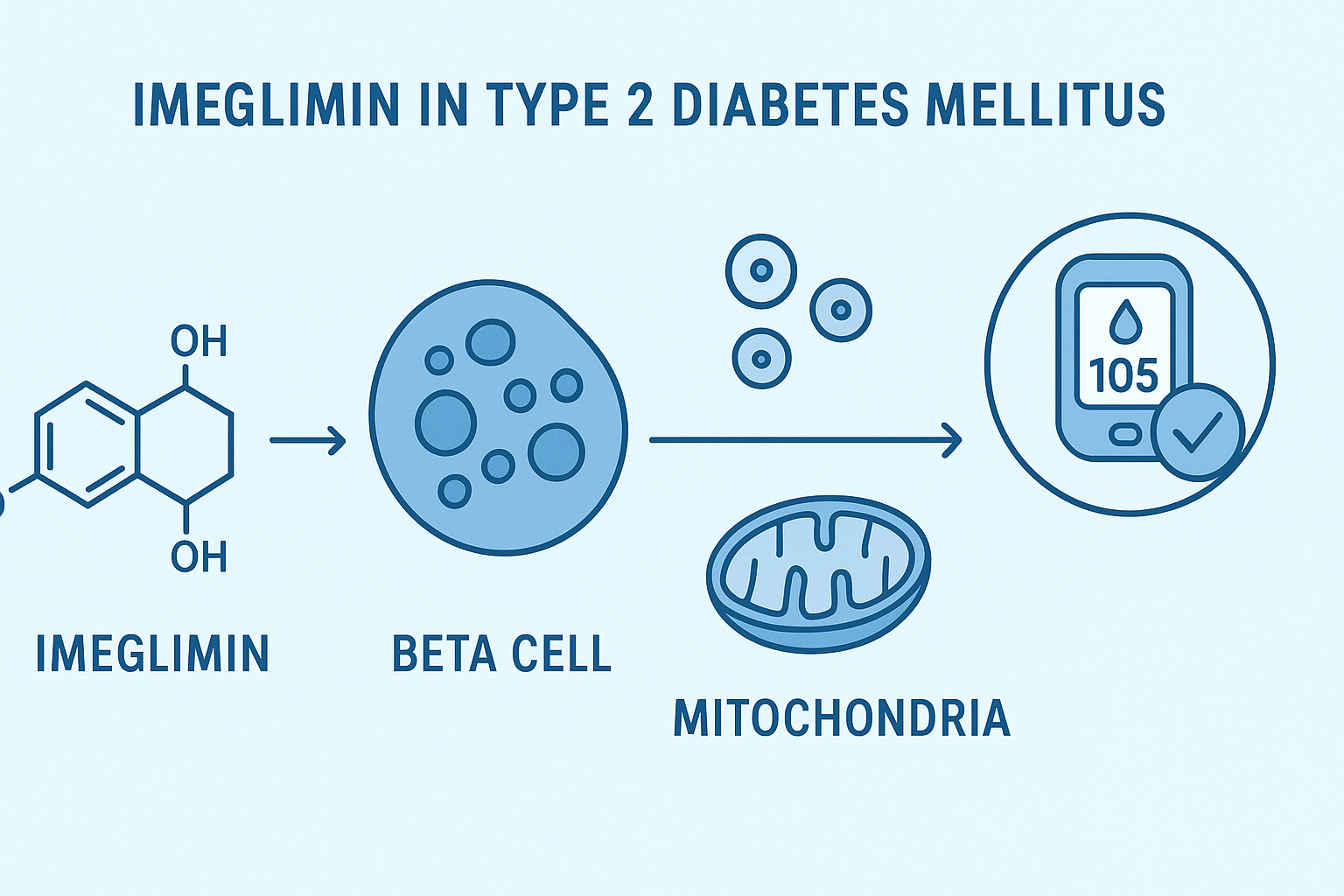
The effect of ginseng supplementation and health outcomes: A GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Ginseng supplementation may improve inflammatory profiles and support cardiometabolic health, according to a comprehensive review of 44 randomized controlled trials.